In this blog, we will go through you the knowledge from titanium material to evetually titanium capillary tubes.
What is titanium?
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It is a strong, lightweight, and highly corrosion-resistant metal. It has a silver color, low density.
The element itself was firstly discovered in 1791 by the British clergyman William Gregor and later isolated in its metallic form in 1910 by the American chemist Matthew A. Hunter.
Titanium is relatively abundant in the Earth’s crust and is the ninth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, with a concentration of approximately 0.57%. However, it is not usually found in its pure form in nature, but rather as titanium dioxide minerals such as ilmenite, rutile, and anatase, or in the form of iron-titanium oxides such as magnetite and hematite.

Titanium is relatively abundant in the Earth’s crust and is the ninth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, with a concentration of approximately 0.57%. However, it is not usually found in its pure form in nature, but rather as titanium dioxide minerals such as ilmenite, rutile, and anatase, or in the form of iron-titanium oxides such as magnetite and hematite.
The resulting titanium dioxide can be further processed through a variety of methods to produce pure titanium metal, such as the Kroll process, which involves reducing titanium tetrachloride with magnesium.
As of 2021, China had the largest reserves of titanium minerals worldwide, amounted to approximately 230 million metric tons of titanium dioxide content that year. China’s entire reserves of titanium are found as ilmenite.
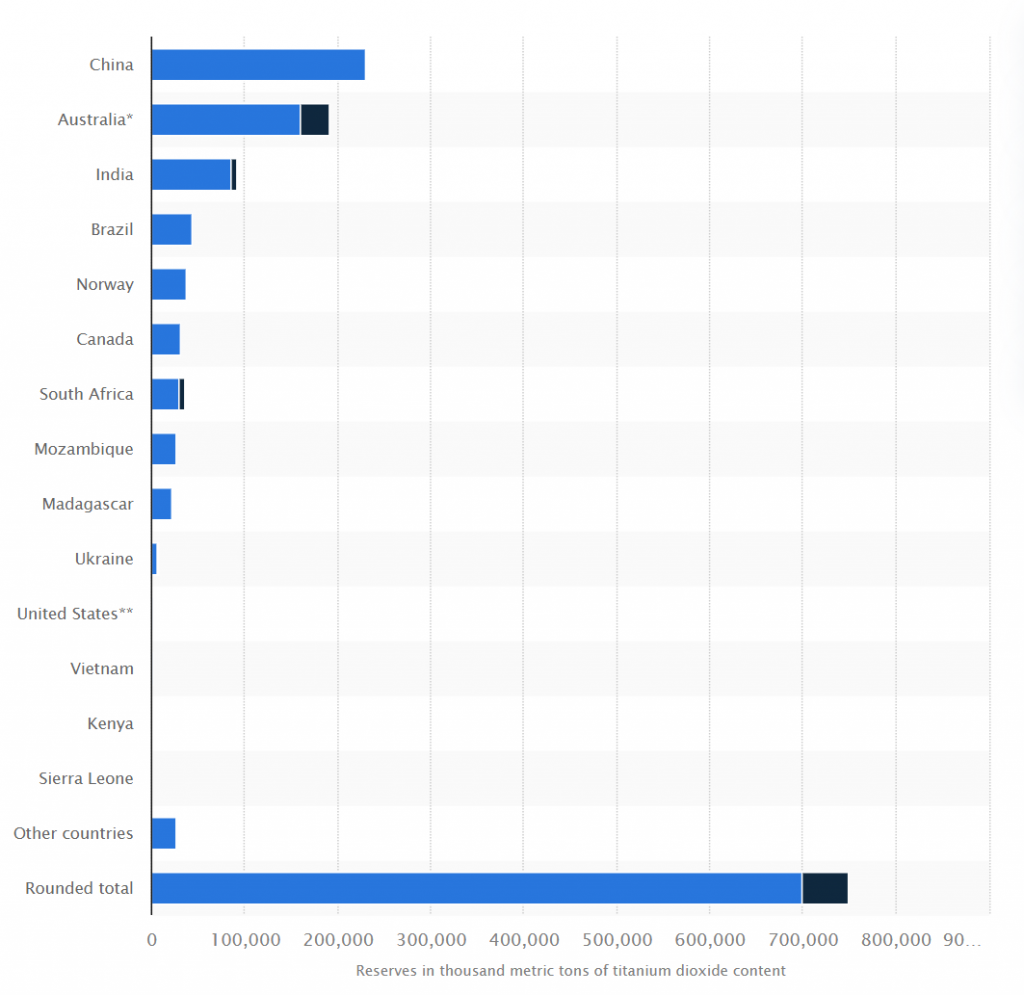
The Chinese government has been actively encouraging the development of its domestic titanium industry to reduce its dependence on imports and increase its self-sufficiency in this critical strategic material.
What can be Titanium shaped to?
Titanium can be formed into various shapes, depending on the specific manufacturing process used.
Sheets and Plates:
They are flat and thin pieces of titanium that can be cut, bent, and rolled into different shapes and sizes. These are used in the aerospace industry for aircraft skin, wings, and structural components, as well as in the chemical and oil and gas industries for tanks, heat exchangers, and reactors.
Bars and rods:
They are cylindrical or rectangular-shaped pieces of titanium that can be used as structural components or machined into bolts, screws, and other fasteners. These are used in the automotive and sports industries for suspension systems, drive shafts, and golf club shafts, as well as in the construction industry for reinforcing bars and dowels.
Tubes and pipes:
They are hollow cylindrical shapes of titanium that can be used in the chemical and petrochemical industries for transporting corrosive fluids and gases, as well as in the medical industry for implantable devices and instruments due to it’s biocompatibility.
Forgings:
They are complex shapes of titanium that are produced by heating and shaping the metal using a forging press. These are used in the aerospace and defense industries for jet engine components, missile casings, and landing gear, as well as in the power generation industry for turbine blades and rotors.
Castings:
These are three-dimensional shapes of titanium that are produced by pouring molten metal into a mold, they are used in the aerospace industry for airframe components, as well as in the medical industry for orthopedic implants and dental prostheses.
Wires:
These are thin, flexible strands of titanium that can be used in the welding and brazing industry for joining other metals, as well as in the medical industry for sutures and orthodontic wires.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium can also form with other materials to alloys that possesses special attributes aiming the application in different fields.
Ti-6Al-4V: This is the most commonly used titanium alloy, which consists of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium. It is strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant, and is used in a variety of applications, such as aerospace, biomedical, and sports equipment.
| Element | Minimum (%) | Maximum (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Bal. | Bal. |
| Aluminum | 5.5 | 6.75 |
| Vanadium | 3.5 | 4.5 |
| Carbon | – | 0.08 |
| Nitrogen | – | 0.05 |
| Oxygen | – | 0.2 |
| Iron | – | 0.3 |
| Hydrogen | – | 0.015 |
| Yttrium | – | 0.005 |
| Other | – | 0.4 (total) |
Ti-3Al-2.5V: This titanium alloy contains 3% aluminum and 2.5% vanadium. It is used in applications where high strength, low weight, and good corrosion resistance are required, such as bicycle frames and surgical implants.
| Element | Minimum (%) | Maximum (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Bal. | Bal. |
| Aluminum | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| Vanadium | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| Carbon | – | 0.08 |
| Nitrogen | – | 0.05 |
| Oxygen | – | 0.15 |
| Iron | – | 0.25 |
| Hydrogen | – | 0.0125 |
| Other | – | 0.4 (total) |
Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo: This titanium alloy contains 6% aluminum, 2% tin, 4% zirconium, and 2% molybdenum. It is used in applications where high strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance are required, such as in the aerospace industry for aircraft components.
| Element | Minimum (%) | Maximum (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Bal. | Bal. |
| Aluminum | 5.5 | 6.5 |
| Sn | 1.8 | 2.2 |
| Zr | 3.6 | 4.4 |
| Mo | 1.8 | 2.2 |
| Carbon | – | 0.08 |
| Nitrogen | – | 0.05 |
| Oxygen | – | 0.2 |
| Iron | – | 0.3 |
| Hydrogen | – | 0.015 |
| Other | – | 0.4 (total) |
Ti-15V-3Cr-3Sn-3Al: This titanium alloy contains 15% vanadium, 3% chromium, 3% tin, and 3% aluminum. It is used in applications where high strength and corrosion resistance are required, such as in the marine industry for propeller shafts and seawater valves.
| Element | Minimum (%) | Maximum (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Bal. | Bal. |
| Vanadium | 14.0 | 16.0 |
| Chromium | 2.5 | 3.5 |
| Tin | 2.5 | 3.5 |
| Aluminum | 2.5 | 3.5 |
| Carbon | – | 0.08 |
| Nitrogen | – | 0.05 |
| Oxygen | – | 0.2 |
| Iron | – | 0.25 |
| Hydrogen | – | 0.015 |
| Other | – | 0.4 (total) |
Titanium Capillary Tube
Titanium capillary tubes are typically produced using a process called cold drawing.

The process involves the following steps:
- Tube preparation: The first step is to prepare the titanium tube for the cold drawing process. This may involve cleaning the tube to remove any surface contaminants or applying a lubricant to reduce friction during the drawing process.
- Tube insertion: The tube is inserted into the draw bench, which consists of a series of dies of decreasing diameter. The tube is held in place by a gripping device, such as a collet, which is attached to a chain or wire rope.
- Tube drawing: The gripping device pulls the tube through the first die, which compresses the tube and reduces its diameter while increasing its length. The tube is then pulled through subsequent dies, each of which has a smaller diameter than the previous die.
- Annealing: After a few passes through the draw bench, the titanium tube may become work-hardened and brittle. To prevent cracking or failure, the tube is annealed, which involves heating the tube to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling it to room temperature. This process relieves stress and softens the material, making it easier to draw through the remaining dies.
- Final pass and finishing: The titanium tube may go through several rounds of drawing and annealing until the desired diameter and length are achieved. After the final pass through the draw bench, the tube may be cut to the desired length and undergo finishing processes, such as polishing or cleaning.
The application of Titanium Capillary Tubes
Titanium capillary tubes are typically used in applications where precise and small-diameter tubing is required. Some common applications for titanium capillary tubes include:
- Medical devices: Titanium capillary tubes are used in various medical devices such as biopsy needles, catheters, marker bands and endoscopes due to their biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength-to-weight ratio.
- Chromatography: Titanium capillary tubes are used as columns in gas chromatography and liquid chromatography due to their high strength, corrosion resistance, and low reactivity with chemical compounds.
- Aerospace and aviation: Titanium capillary tubes are used in the aerospace and aviation industry as fuel and hydraulic lines, and other small diameter tubing where lightweight, high strength and corrosion-resistant material is required.
- Precision instruments: Titanium capillary tubes are used in the manufacturing of various precision instruments such as sensors, probes, and measurement equipment due to their strength, durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Electronics: Titanium capillary tubes are used in various electronic applications as wire insulation, heating elements, or as components for electronic sensors.
Stahlmann is one of the leading manufacturer of Titanium Capillaries in China, we offer titanium capillary tubes with below sizes and materials:
Material: Gr.1, Gr.2, Gr.9
Outside Diameter: 0.2 – 8 mm (0.00787 – 0.315 in.)
Wall Thickness: 0.015 -0.5 mm (0.00197 -0.0787 in.)
Tolerance: OD:+/-0.003mm, ID:+/-0.005mm, LG:+/-0.05mm
Please feel free to contact us for inquiries.





