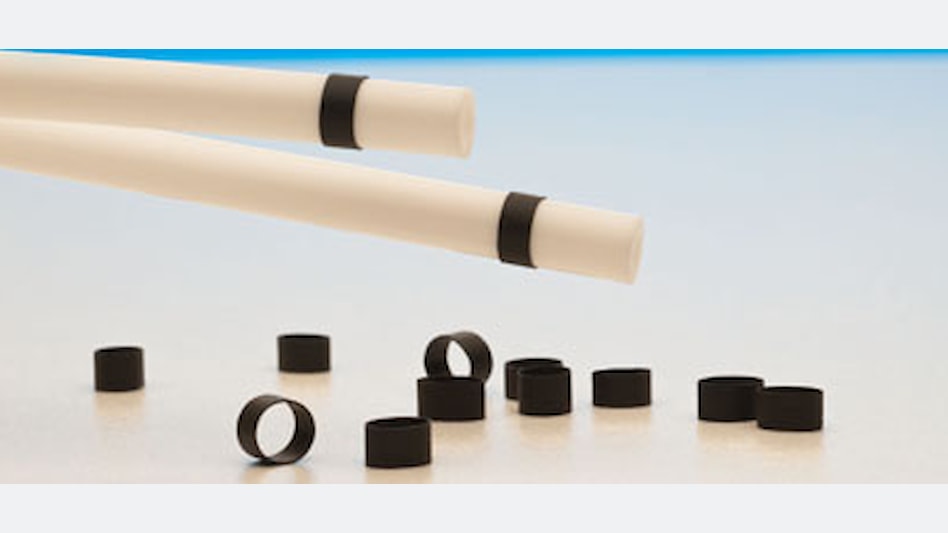
What is a marker band?
In the context of medical equipment, marker bands are thin-walled tubes made of biocompatible metals such as gold, platinum, tantalum, iridium, or tungsten. (to find more about tantalum marker bands, please see other blog “tantalum marker bands“
Marker Bands are also called: radiopaque markers, catheter markers, image ring, position markers, identification markers.
What are the materials of marker bands
Common materials used for marker bands include:
- Gold: Gold is a biocompatible metal that is widely used for marker bands due to its durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Platinum: Platinum is another biocompatible metal that is widely used for marker bands. It is a more expensive option than gold, but has similar properties.
- Tantalum: Tantalum is a biocompatible metal that is used for marker bands due to its resistance to corrosion and biocompatibility.
- Iridium: Iridium is a biocompatible metal that is used for marker bands due to its durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Tungsten: Tungsten is a biocompatible metal that is used for marker bands due to its strength and durability.
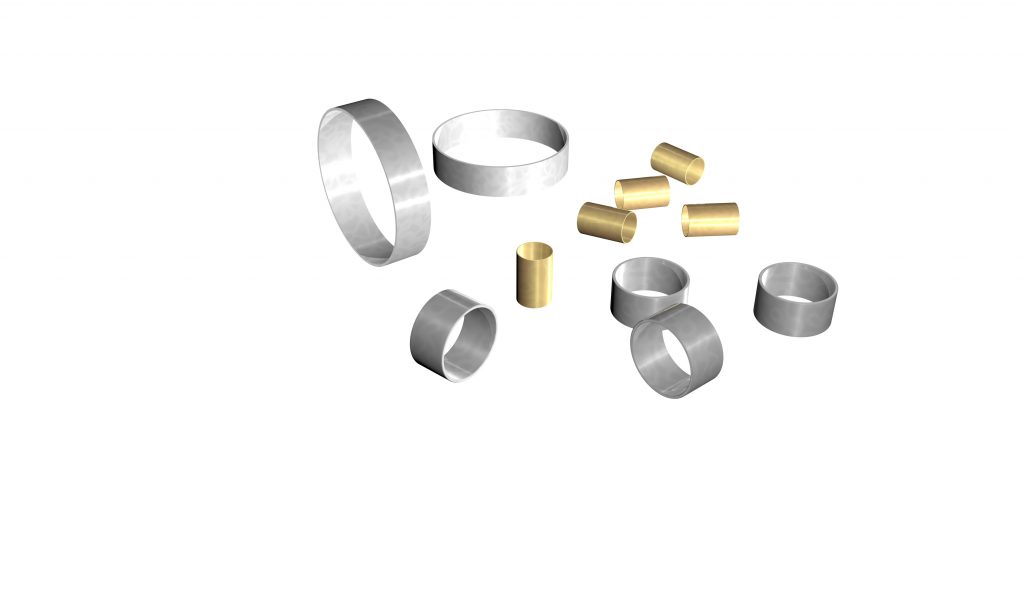

plastic marker bands are also used in medical equipment. They are made from biocompatible plastics, such as polycarbonate, polypropylene, or polyethylene, and are used for applications where metal marker bands are not suitable.

Plastic marker bands offer several advantages over metal marker bands, including being lighter, less expensive, and easier to produce. They are also more flexible and can be used on equipment with curves or angles that would be difficult to mark with metal marker bands.
However, plastic marker bands may not be as durable as metal marker bands and may not be suitable for certain medical procedures that require exposure to high heat or pressure. They also may not have the same level of accuracy in markings as metal marker bands.
The choice between plastic and metal marker bands will depend on the specific needs of the medical procedure and the equipment being used. In some cases, both types of marker bands may be used together in a single medical device.
What are marker bands used for?
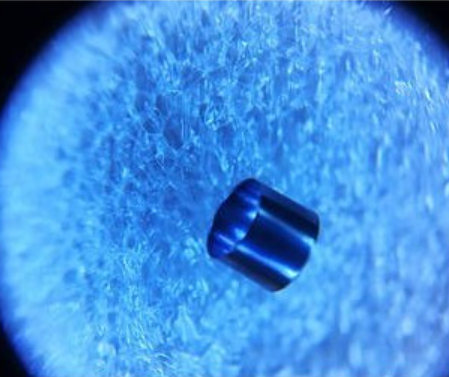
They are used to mark the location of catheters, guide wires, or other medical instruments within the body during medical procedures. The use of marker bands helps to ensure that medical instruments are properly positioned and can provide important information for monitoring and interpreting the results of the procedure.
The marker bands are mechanically crimped or swaged onto the desired location of the instrument and provide a visual reference for its position within the body, which can aid in the accuracy and safety of the procedure.
How are marker bands made?
Marker bands are typically made by machining biocompatible metals such as gold, platinum, tantalum, iridium, or tungsten into short, thin-walled tubes. The tubes are then mechanically crimped or swaged onto the desired location of the catheter, guide wire, or other medical instrument.
The process of machining the marker bands involves cutting and shaping the metal into the desired shape and size using specialized equipment and techniques. The crimping or swaging process involves using a tool to deform the metal into the desired shape, thereby attaching the marker band to the medical instrument.
The goal of the marker band manufacturing process is to produce a product that is
- Biocompatibility: Marker bands must be made of materials that are biocompatible with the human body and do not cause adverse reactions.
- Durability: Marker bands must be able to withstand the conditions of the medical procedure, including exposure to heat, pressure, and other factors, without breaking or coming loose.
- Accuracy of markings: The markings on the marker bands must be accurate and easily visible to ensure proper placement of the medical instrument.
- Sterilization: Marker bands must be able to be sterilized to meet the requirements of the medical procedure and prevent the spread of infection.
- Regulatory compliance: Marker bands must meet the relevant regulatory standards and requirements, such as those set by the FDA in the US or the CE mark in Europe.
The quality of the marker bands is carefully controlled to ensure that they meet the required standards for use in medical applications.
Embedding Marker Bands vs. Swaging
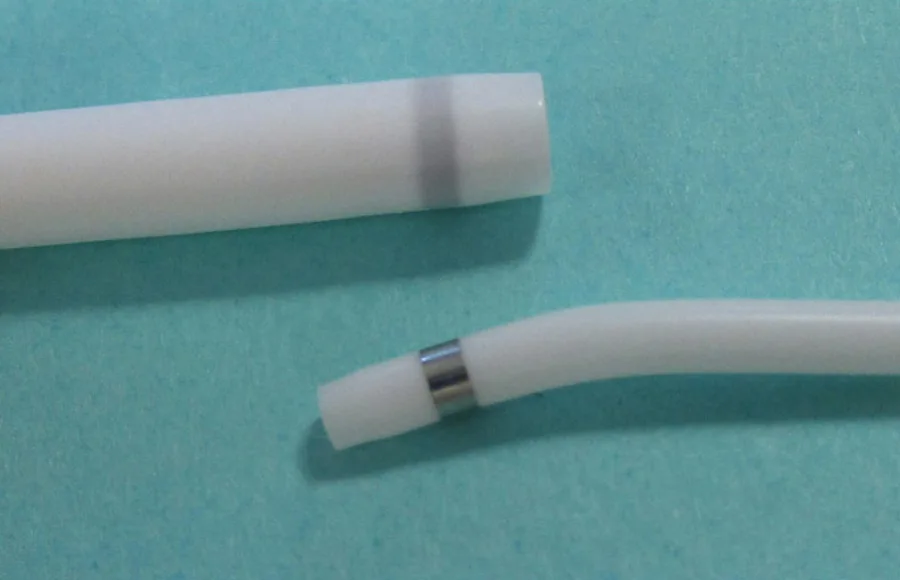
Embedding and swaging are two methods used to attach marker bands to medical equipment. The main differences between the two methods are:
Embedding: This method involves inserting the marker band into a groove or indentation in the medical equipment and crimping it into place. Embedding provides a secure and permanent attachment and can be done on equipment with curves or angles.
Swaging: This method involves compressing the marker band around the medical equipment to form a tight grip. Swaging is typically used on equipment with straight sections and provides a secure and permanent attachment.
What are the benefits of embedding marker bands VS Swaging Marker Bands
The benefits of embedding marker bands as opposed to swaging include:
- Improved durability: Embedding the marker band within the wall of the medical instrument can provide greater durability and resistance to wear and tear compared to swaging.
- Reduced risk of dislodgement: The embedded marker band is less likely to come loose or become dislodged compared to a swaged marker band.
- Improved imaging: Embedding the marker band can result in improved visibility on medical imaging, allowing for more accurate monitoring of the instrument’s position within the body.
- Reduced potential for patient irritation: Embedding the marker band eliminates the potential for the marker band to irritate the patient, as it is no longer in direct contact with the body.
While swaging sure can be a better option when it comes:
- Cost-effectiveness: Swaging may be a more cost-effective option for attaching marker bands, especially for disposable medical instruments.
- Ease of use: Swaging marker bands onto medical instruments can be a simpler and quicker process compared to embedding them.
- Flexibility: Swaged marker bands can be easily removed or replaced if necessary, making them a good option for situations where the position of the marker band may need to be adjusted.
- Compatibility with existing equipment: In some cases, existing medical equipment may not be compatible with embedded marker bands and may require the use of swaged marker bands.
It is important to consider the specific requirements of the medical procedure and the equipment being used when deciding between swaging and embedding marker bands. Both methods have their benefits and limitations, and the most appropriate option will depend on the particular situation.